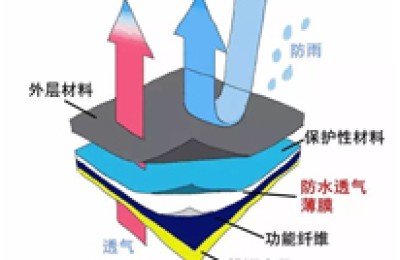
Flocked clothis a product that uses high-voltage electrostatic fields to plant short fibers on gray cloth. That is, an adhesive is printed on the surface of the substrate and then recycled. The electrostatic field of a certain voltage causes the short fibers to be vertically accelerated and transplanted onto the gray cloth coated with adhesive. Contents1Process introduction2Flocked fabric analysis3Process flow Adhesive coating, flocking, drying, baking and cleaningProcess IntroductionEditorWith the rapid development of electronics, fiber, chemical, machinery and other industries, flocking The quality of cloth continues to improve and its uses expand. It has gradually developed from the original industrial fabrics and decorative fabrics to the field of clothing fabrics. In recent years, the development has been particularly rapid, and more and more new varieties have been developed. Many printing and dyeing methods have been applied to flocked cloth, such as paint printing, hot stamping printing, printed cloth flocking and direct printing and drawing on flocked cloth. Dye printing. The use of these methods has enriched cloth flocking products and added a beautiful landscape to the clothing industry. Analysis of flocked fabricsEditIt is necessary to carry out various For printing, you must have a comprehensive understanding of the structure and performance of flocking cloth. Although its processing process is simple, it also involves the reasonable cooperation of electrochemical, fiber and mechanical technologies to ensure the best style of flocking products, and flocking cloth needs to be Reprinting, in which the selection of pile, binder and dye for dyeing the pile is crucial. 1. VelvetFrom the perspective of flocking, the most commonly used fluff is viscose and nylon fiber. Viscose fiberis made from wood as raw material through certain chemical processing. The crystallization area of the fiber is 30~40%. The degree of polymerization is around 250~500. Because the crystallization area of viscose fiber is relatively high, dyes are not easy to penetrate. Generally, it is difficult to obtain good blackness when dyeing black, and special dyes and dyeing methods must be used. At the same time, due to its low degree of polymerization, the fiber strength is far less than that of nylon. Generally, dyes suitable for viscose fibers include direct, reactive, vulcanized, etc. Naftolis also acceptable, but should be used sparingly. Viscose does not soften or melt at high temperatures, and begins to discolor and decompose at 260~300°C. Nylon fiber is an organic diacid and diamineAmino acidorPropionamideis a raw material throughacylA polymer material connected by amine bonds. Nylon fiber has good elasticity, high strength, wear resistance and durability. It is a thermoplastic fiber. The commonly used ones are nylon 6 and nylon 66. Nylon fiber has good elasticity and luster, but nylon 66 will turn yellow at 150°C, become sticky and soften at 230°C, and melt at 250°C; while nylon 6 will soften at 180°C and melt at 215°C. Therefore, in the process of wool dyeing, flocking and printing, it is necessary to first understand what kind of fiber it is, so that the dye and process can be correctly selected according to its performance, so as not to cause unnecessary losses during the processing2. AdhesiveThe adhesive selected for flocking plays an important role in the printing and dyeing post-processing industry. Commonly used adhesives are divided into external-linking adhesives and self-cross-linking adhesives. Externally linked adhesives contain carboxylic groups(-C00H) or amide groups (-C-NH2), amino groups ( –NH3) can be combined with external cross-linking agentThe functional group undergoes cross-linking reaction. During film formation, it can react with the external adhesive to form a mesh-like film, thereby fixing the villi on the base fabric. Self-crosslinking adhesives contain groups in the molecule that make the molecular chains self-crosslink, for exampleHydroxyMethyl (-CH2-OH), epoxy group (-CH- CH2), and also has a hydroxymethylacrylamide that can participate in copolymerization (CH2=CH-CONH CH2OH) or glycidyl methacrylate(CH2=C-COOCH2- CH-CH2) opens the double bonds to participate in the reaction when copolymerized with other monomers. At present, these two adhesives are used in flocking. When using the external linking adhesive, a certain amount of Cross-linking agent, catalyst, but it must be used immediately after preparation, especially after adding the catalyst, it cannot be left for too long, otherwise cross-linking will occur at room temperature and affect the use. This should be noted during operation. The effective placement time of self-crosslinking adhesive is relatively long. If a small amount of cross-linking agent is added during use, increasing the cross-linking depth will be more conducive to improving flocking fastness. So what is the relationship between adhesives and flocking technology and printing? Many factories dedicated to flocking printing suffer from partial lint loss due to incompatible processes. In addition to the fastness of the adhesive, the baking temperature and time of flocking are very important, that is, they mustThe adhesive must be fully cross-linked without damaging the pile. Generally speaking, there are several requirements for the selection of flocking adhesive: 1) The adhesive must have a strong bonding force to the gray fabric and fluff, and the feel must be soft. 2) The viscosity is moderate and its chemical stability is good. It is suitable for rotary screen scraping and will not block the screen. 3) It is resistant to washing and meets the fastness indicators of various clothing fabrics. 4) It is easy to operate, harmless to the human body, and is a green and environmentally friendly product. 3. DyeingDyeing fluff is a very important link in flocking fabrics. The color, light, physical and chemical indicators of the fluff after dyeing must meet certain requirements. From the perspective of flocking, the down dyeing must first satisfy the alignment of the color light and the non-recoloration during the baking process after flocking. If printing is to be carried out after flocking, the dyed fluff must be able to withstand every step of the entire printing process, and the flocking cloth must have good stability in steaming, hot water washing or soaping, and acid and alkali. If discharge printing is done, the dye in the dyed fluff must not be resistant to reducing agents, which is very important for the selection of dyes during dyeing, otherwise the discharge whiteness will be different each time, even if it is uniformPrinting technology will also produce different products, so that it can only produce some self-sold products but cannot take orders. This is a failure in flock release printing. Generally speaking, the selection of dyeing dyes must meet the following requirements: 1) The color matching dyes should have good compatibility and similar dyeing curves. 2) Various color fastness indicators of dyes meet customer requirements. 3) In discharge printing, the dye used to dye the fluff must be intolerant to reducing agents and have good discharge whiteness. Generally, semi-discharge dyes cannot be used. Processing processEditApplying adhesiveThe viscosity of the adhesive should be controlled between 15,000 and 30,000 cp. If the viscosity is high, it will be difficult for the fluff to penetrate deeply into the base fabric, causing the fluff to fall off due to insufficient bonding strength. If the viscosity is too low, it will easily penetrate into the base fabric. Although the fluff can penetrate into the inner layer of the adhesive and improve the wear resistance, it feels hard. Therefore, the thickness of the adhesive layer is preferably 0.2 to 0.4 mm. FlockingThe amount of hair given for flocking affects the quality of the flocked fabric. If the amount of hair given is insufficient, the density of flocking will be insufficient; If the amount is too much, most of the fluff will be stuck to the base fabric by the adhesive, and the remaining fluff that is not stuck by the adhesive will continue to fly up and down under the action of the electric field, affecting indoor cleaning. Drying and bakingThe purpose of pre-baking is to remove the organic solventAnd the water evaporates. Generally around 80℃. The purpose of baking is to improve the fastness, that is, to firmly combine the adhesive with the fluff and base fabric. If the temperature is low, the fixing fastness cannot be achieved. If the temperature is high, the catalyst in the adhesive will precipitate acidic substances and the base fabric will be vulcanized. The temperature is generally controlled at 150±5℃. Cleaning
The purpose of cleaning is to recycle the floating brush that has not been implanted with adhesive on the flocked fabric